
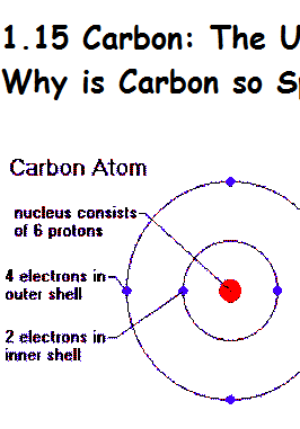
Unstable isotopes most commonly emit alpha particles (He 2+ ) and electrons. All three have six protons, but their neutron numbers - 6, 7, and 8, respectively - all differ. Carbon-14 (14 C) is unstable and only occurs in trace amounts. And so eventually, the C-14 atom undergoes a change to N-14, in which one neutron. There are three isotopes of carbon found in nature carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The Group 14 elements tend to adopt oxidation states of +4 and, for the heavier elements, +2.
Each of these elements has only two electrons in its outermost p orbital: each has the electron configuration ns2np2. As a result, carbon-14 is continuously formed. Carbon-14 can also be produced in the atmosphere by other neutron reactions, including in particular 13C(n,)14C and 17O(n,)14C. Nuclear decay reactions occur spontaneously under all conditions, whereas nuclear transmutation reactions are induced. Eight neutrons is just too much of a good thing when there are only 6 protons. The carbon family, Group 14 in the p-block, contains carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl). Radioactive carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years and undergoes decay, where the neutron is converted into a proton, an electron, and an electron antineutrino. We begin this section by considering the different classes of radioactive nuclei, along with their characteristic nuclear decay reactions and the radiation they emit. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.
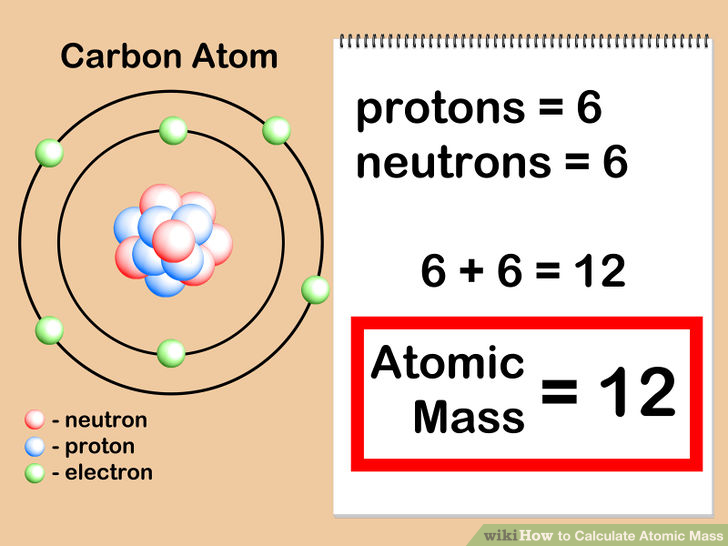
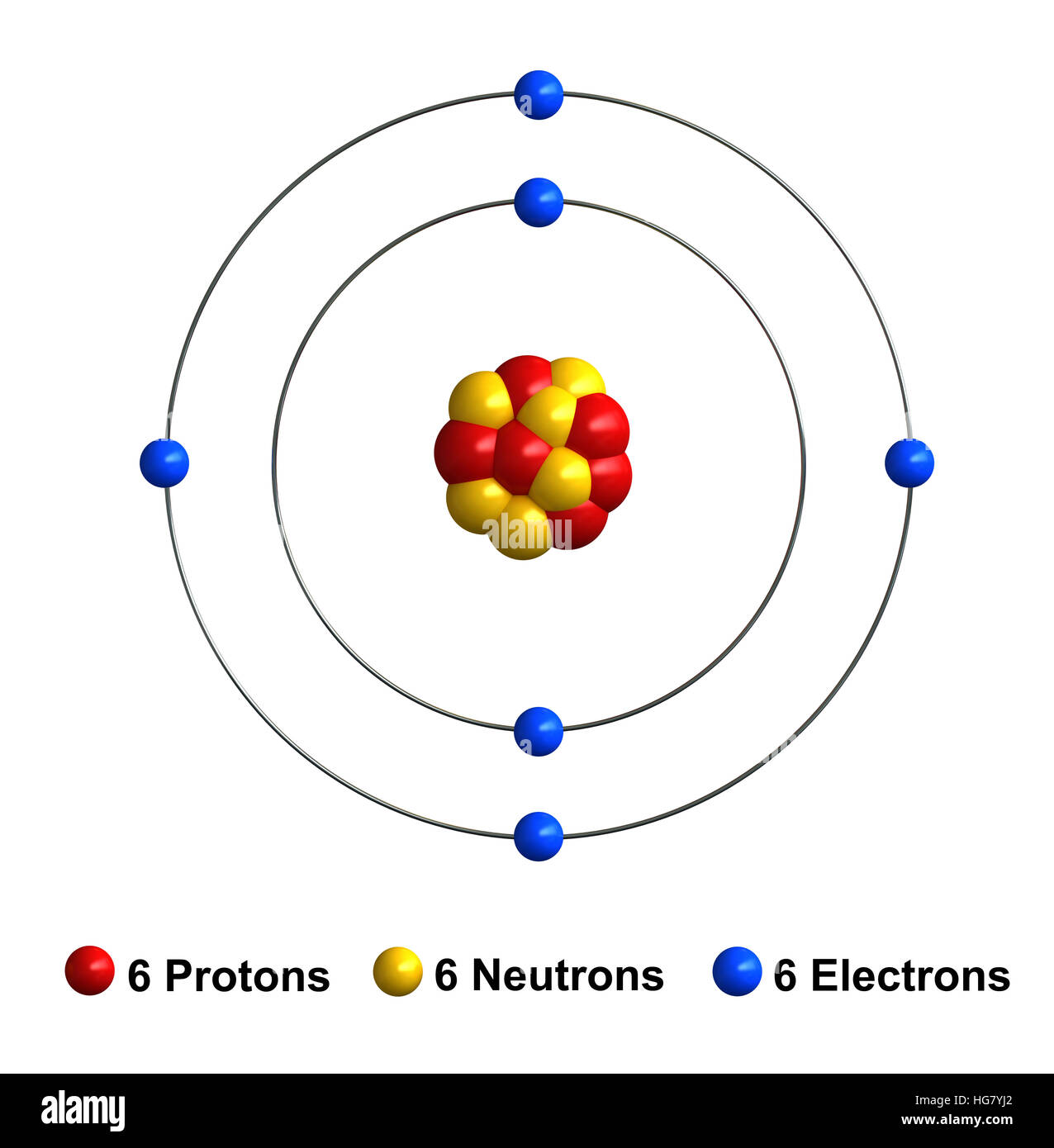
As we shall see, nuclear decay reactions occur spontaneously under all conditions, but nuclear transmutation reactions occur only under very special conditions, such as the collision of a beam of highly energetic particles with a target nucleus or in the interior of stars. Element Carbon (C), Group 14, Atomic Number 6, p-block, Mass 12.011. In contrast, in a nuclear transmutation reaction, a nucleus reacts with a subatomic particle or another nucleus to form a product nucleus that is more massive than the starting material. Protons and neutrons, collectively called nucleons, are packed together tightly in a nucleus. Based on the trend with carbon and the fact that plutonium has 94 protons, how many neutrons are in radioactive plutonium-244 A. For example, 6 14 C 6 14 C is called carbon-14. Carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons, while carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. The resulting daughter nuclei have a lower mass and are lower in energy (more stable) than the parent nucleus that decayed. Elemental carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. In a nuclear decay reaction, also called radioactive decay, an unstable nucleus emits radiation and is transformed into the nucleus of one or more other elements. The two general kinds of nuclear reactions are nuclear decay reactions and nuclear transmutation reactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
